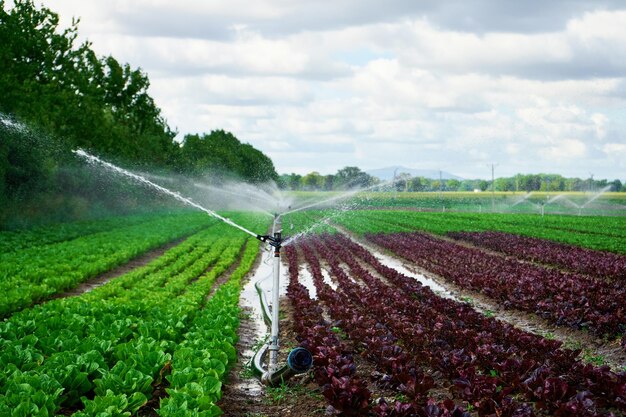
Small-scale farming plays a crucial role in Zambia’s economy, providing food security and livelihoods for millions. However, with challenges such as climate change, soil degradation, and limited resources, adopting effective farming practices is essential for sustainable agriculture. Here are ten best farming practices that small-scale farmers in Zambia can implement to improve productivity and ensure long-term success.
1. Soil Health Management
Maintaining healthy soil is fundamental for successful farming. Small-scale farmers should adopt practices such as crop rotation, cover cropping, and the application of organic fertilizers (like compost and manure) to enhance soil fertility and structure. Regular soil testing can help farmers understand nutrient deficiencies and adjust their soil management practices accordingly.
2. Conservation Agriculture
Conservation agriculture involves minimal soil disturbance, maintaining soil cover, and practicing crop rotation. This method helps prevent soil erosion, improves water retention, and enhances biodiversity. Farmers can implement techniques like no-till farming and using mulch to protect the soil, leading to increased yields and reduced input costs.
3. Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
Implementing IPM strategies can help small-scale farmers control pests and diseases while minimizing the use of chemical pesticides. Farmers should encourage beneficial insects, rotate crops, and use traps or natural repellents to manage pest populations. Educating themselves about pest life cycles and resistant crop varieties can further enhance their IPM efforts.
4. Water Management
Efficient water management is essential, especially in areas prone to drought. Farmers can adopt practices like rainwater harvesting, drip irrigation, and mulching to conserve moisture. Additionally, scheduling irrigation based on crop needs and local weather forecasts can optimize water usage, ensuring crops receive adequate moisture without wasting resources.
5. Diversification of Crops and Livestock
Diversifying crops and livestock can reduce risks associated with market fluctuations and climate change. Farmers should consider growing a mix of staple crops, vegetables, and legumes, along with raising small livestock or poultry. This diversification enhances food security and provides various income sources, contributing to a more resilient farming system.
6. Use of Improved Seeds
Utilizing improved and certified seeds can significantly enhance crop yields and resilience to pests and diseases. Small-scale farmers should invest in quality seeds, focusing on varieties that are well-suited to their local conditions and climate. Collaborating with local agricultural extension services can help farmers access the best seed options and receive advice on proper planting techniques.
7. Organic Farming Practices
Incorporating organic farming methods can improve soil health, increase biodiversity, and reduce reliance on chemical inputs. Small-scale farmers should consider using organic fertilizers, crop rotations, and natural pest control methods to maintain an eco-friendly approach. Not only does organic farming support sustainability, but it can also appeal to consumers seeking healthy food options.
8. Post-Harvest Management
Effective post-harvest management is crucial for minimizing losses and maximizing profits. Farmers should invest in proper storage facilities, drying methods, and transportation to maintain the quality of their produce. Educating themselves about post-harvest handling techniques can help farmers reduce spoilage and enhance marketability.
9. Training and Education
Continuous learning is vital for improving farming practices. Small-scale farmers should seek training opportunities through agricultural extension services, workshops, and farmer groups. Engaging with other farmers and sharing experiences can provide valuable insights into best practices and innovative solutions to common challenges.
10. Market Access and Cooperatives
Building strong market connections is essential for small-scale farmers to sell their produce at fair prices. Joining or forming cooperatives can help farmers gain collective bargaining power, access better markets, and share resources. Collaborating with local organizations can also provide valuable support in marketing, distribution, and accessing financial services.
By adopting these best farming practices, small-scale farmers in Zambia can enhance their productivity, sustainability, and resilience against challenges. Emphasizing soil health, water management, diversification, and continuous learning will empower farmers to create thriving agricultural systems that contribute to food security and economic growth. As they implement these practices, they will not only improve their livelihoods but also play a vital role in building a sustainable future for Zambia’s agricultural sector.